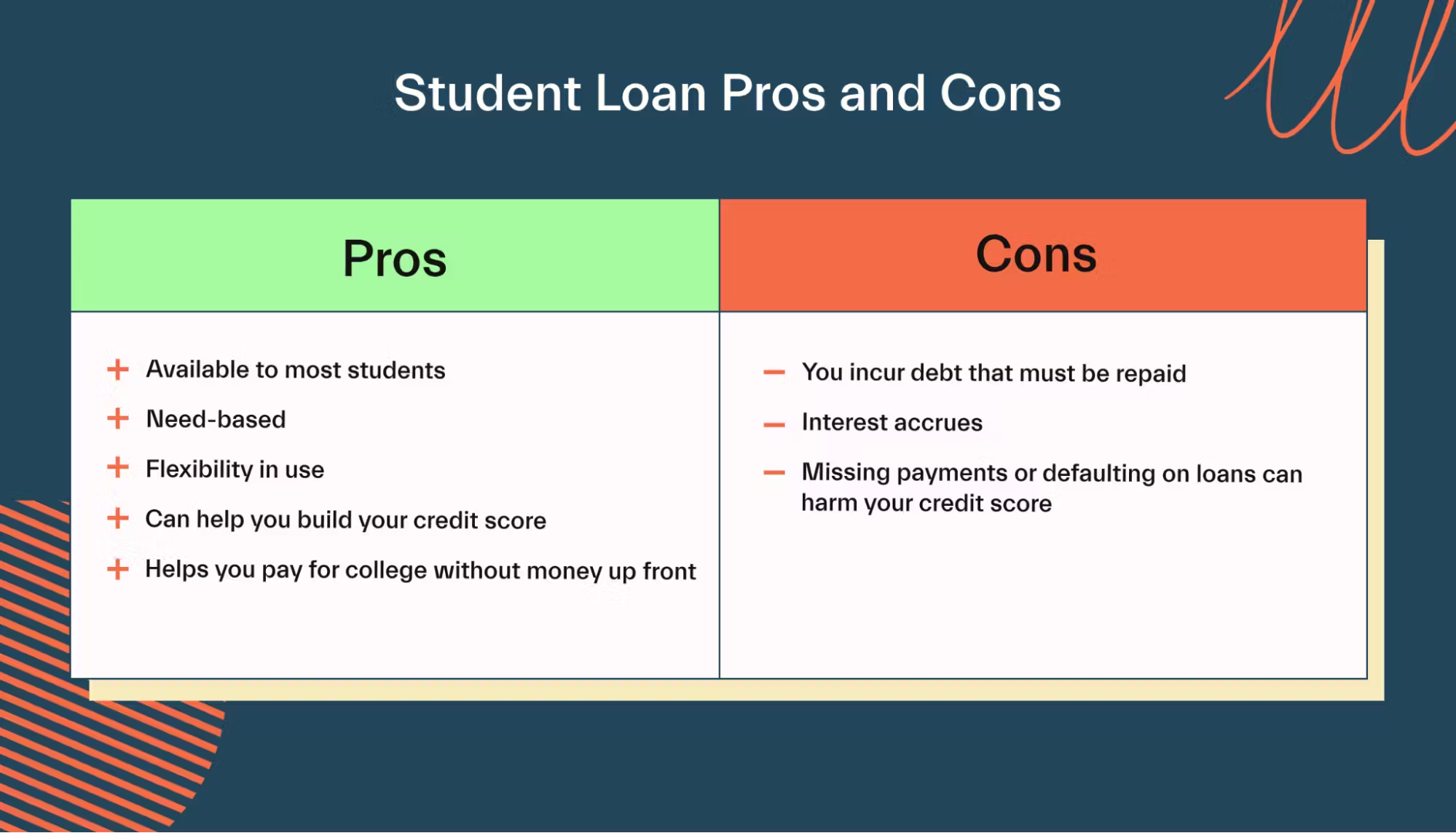
1. Pros of Student Loans
Student loans can offer several advantages, especially for those who may not have other means to afford college or university education.
1.1. Access to Higher Education
- Financial Support: Student loans provide financial assistance to cover tuition, books, and living expenses. This support makes higher education accessible to more students, especially those from low-income backgrounds.
- Investment in Future Earnings: Obtaining a degree often leads to better job opportunities and higher earning potential. Student loans can be seen as an investment in one’s future career and financial stability.
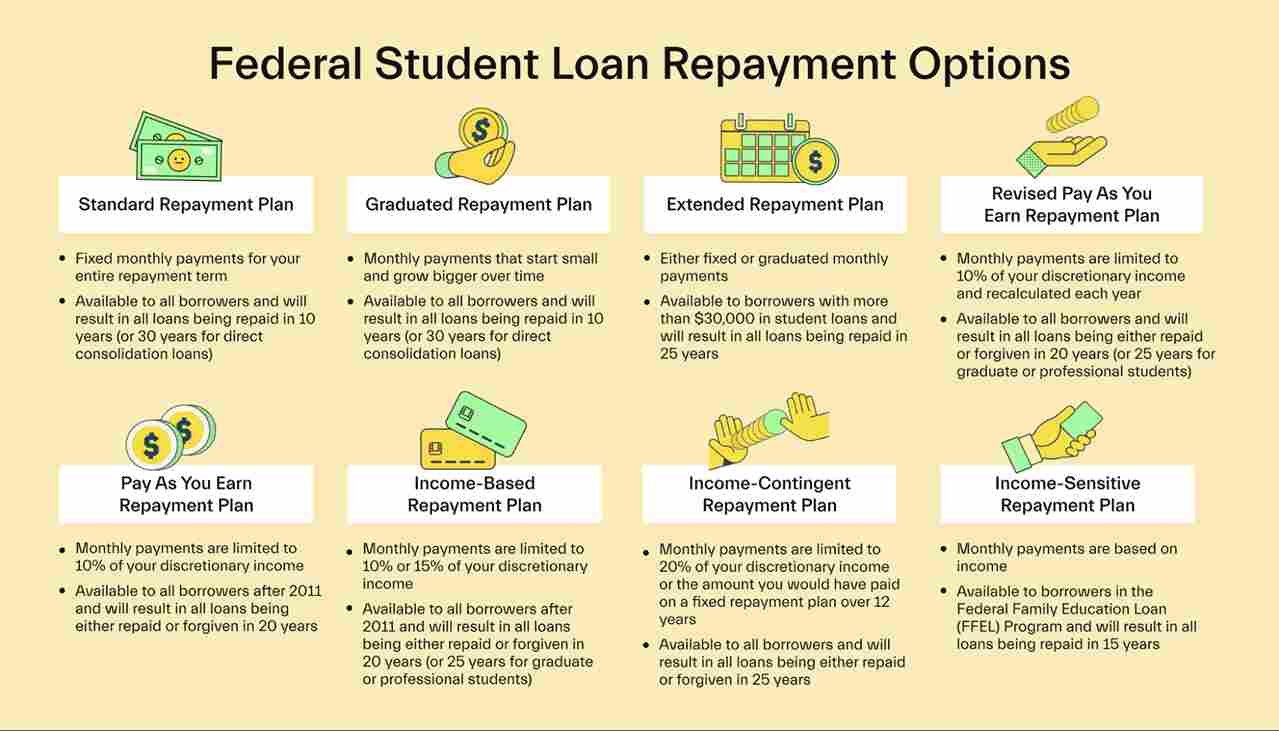
1.2. Flexible Repayment Options
- Variety of Repayment Plans: Federal student loans, in particular, offer several repayment plans, including income-driven repayment (IDR) plans that base monthly payments on your income level. This flexibility can make repayment more manageable.
- Grace Period: Most student loans offer a grace period of six months after graduation before repayment begins. This time allows graduates to find employment and get financially settled.
1.3. Low-Interest Rates for Federal Loans
- Competitive Rates: Federal student loans generally have lower interest rates compared to private loans or credit cards. Lower rates mean paying less interest over the life of the loan.
- Fixed Rates: Unlike some private loans, federal student loans have fixed interest rates that do not change over time, providing predictability in budgeting.
1.4. Opportunity to Build Credit
- Credit Building: Successfully repaying a student loan can help establish and build your credit history. A good credit score can benefit you in future financial endeavors, such as buying a house or getting a car loan.
2. Cons of Student Loans
While student loans offer many benefits, they also have several downsides that students should consider.
2.1. Accumulation of Debt
- Long-Term Debt Burden: Taking out student loans means committing to years, sometimes decades, of repayment. For many graduates, this long-term debt can be a significant financial burden that affects other life decisions, such as buying a home or starting a family.
- High Total Repayment Amount: Due to interest accrual, the total amount repaid can be significantly higher than the original loan amount. The longer it takes to repay, the more interest accumulates.
2.2. Interest Accumulation
- Interest Compounding: Even if payments are deferred while in school, interest continues to accumulate, particularly for unsubsidized loans. This means you could owe more than you borrowed by the time repayment begins.
- Capitalized Interest: If you defer payments, the unpaid interest may be added to the loan principal. This capitalization increases the total loan balance, leading to higher future payments.
2.3. Limited Bankruptcy Relief
- Hard to Discharge: Unlike most other types of debt, student loans are notoriously difficult to discharge in bankruptcy. To get relief, you must prove “undue hardship,” which is a challenging standard to meet.
- Limited Legal Protections: Failing to repay student loans can lead to wage garnishment, tax refund seizure, and other severe financial consequences. These loans often lack the consumer protections available for other debt types.
2.4. Potential for Default and Financial Stress
- Risk of Default: Failing to make loan payments can result in default, which damages your credit score and can have long-term financial consequences.
- Financial Stress: High monthly payments and growing interest can lead to significant financial stress, especially for those who struggle to find well-paying jobs after graduation.
3. Important Considerations Before Taking Out a Student Loan
Before deciding to take out a student loan, consider other options that may help fund your education.
3.1. Explore Scholarships and Grants
- Free Money: Scholarships and grants do not need to be repaid and can significantly reduce the need for student loans. Research and apply for as many as possible.
3.2. Consider Part-Time Work or Work-Study Programs
- Earning While Learning: Part-time jobs or work-study programs can provide additional income to help cover living expenses, reducing the amount you need to borrow.
3.3. Understand the Terms of Your Loan
- Read the Fine Print: Ensure you understand the interest rates, repayment terms, and any fees associated with the loan. Being fully informed can prevent surprises and help you manage your debt effectively.
Conclusion
Student loans can be a valuable tool for financing education, but they come with significant responsibilities and potential risks. Understanding both the pros and cons is essential to making an informed decision. If managed wisely, student loans can be a stepping stone to a brighter future. However, careful planning, budgeting, and exploring alternative funding sources are crucial to avoid the downsides of long-term debt.